
image via rafaelaraujoart.com
为什么建筑师需要数学?看看这5个理由
Why Architects Need Maths? Check Out These 5 Reasons
由专筑网李韧,杨帆编译
“建筑师是个工程师,都是与数学无缘的人”,毫无疑问,你听说过这些言论,但这些一定不正确,如果你还没有在建筑领域迈出第一步,那么你千万不要被这种说法所欺骗,建筑学绝对离不开数学。建筑师需要数学,但他们和真正研究数学的人的应用领域完全不同,有人可能会说,建筑师的数学很简单,但他们可能没有听说过黄金比例和参数化设计。随着建模和概念设计工具的快速发展,一些额外的数学知识可能会让你更具竞争力。现在,让我们看看建筑师需要数学的5个原因。
“Architects are engineers who can’t do maths.” Undoubtedly, you have heard this, or something along these lines by now, but the statement is definitely not true, and if you are yet to take your first steps in the field of architecture, don’t get deceived by such claims, for you absolutely need maths. Architects need maths and do maths, but their applications are just quite a bit different, maybe unique. Some might say that architects’ maths is simple, but they haven’t probably heard of the golden ratio and parametric design. With the rapid advancement in modeling and conceptual design tool, some extra knowledge of mathematics might put you in a much better position. Now, check out our 5 reasons of why architects need maths.
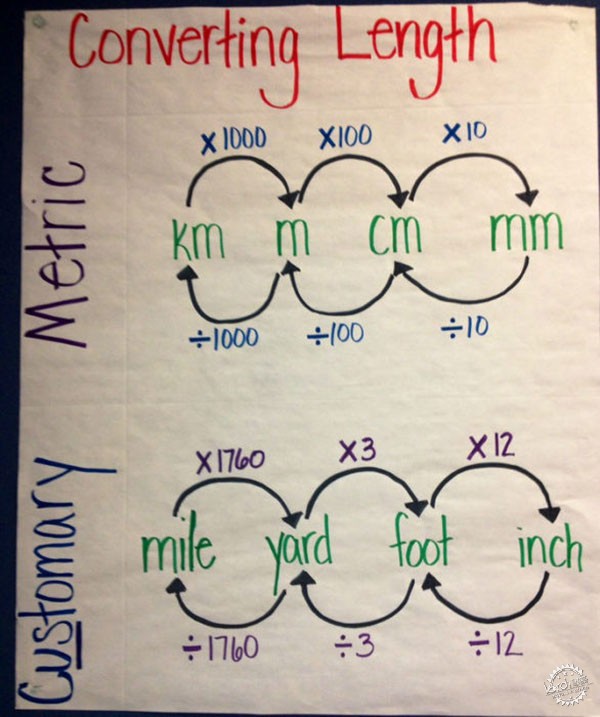
Image via pefourth.weebly.com/math
1、转换单位
这是建筑师面临的最早的任务之一,这需要基本的数学知识。建筑师需要处理许多面积与高差问题。如果你是使用公尺法的大多数人之一,那么你需要知道如何将厘米转换到米,或将米转化为公里,同时你还需要知道如何计算面积,并将它们从平方米转化到公顷等等。如果你是美国人,那么你将需要知道如何从英寸转化到英尺、从英尺转化到英里,以及从平方英尺转化到英亩。如果你的算法以国际为标准,那么你将需要知道如何从一个系统转换到另一个系统,如从英尺转化到米,从英里转化到公里,从英亩转化到公顷。
1-Convert Units
This is one of the earliest tasks an architect faces in the field which requires basic maths knowledge. Architects deal mostly with areas and heights. If you belong to the majority that uses the metric system you need to know how to convert measurements from centimeter to meter and from meter to kilometer. You also need to know how to calculate areas and convert them from meter square to hectare and so. If you are American then you will need to know how to convert from inches to feet and from feet to miles, as well as from square feet to acres. If your practice is international, then you will need to know how to convert from one system to the other, like from feet to meters, from miles to kilometers, and from acres to hectares.
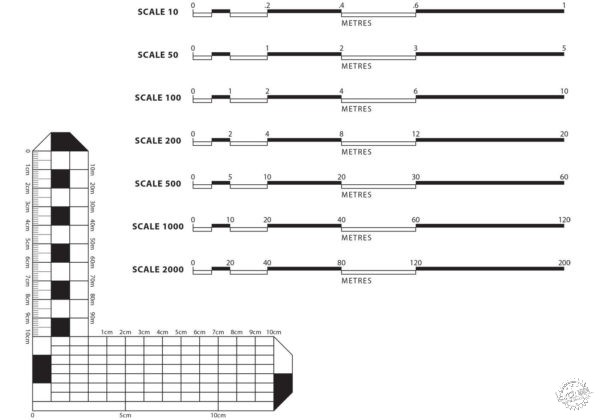
Image via tonobanquetes.com
2、计算规模
在建筑生的第一个设计任务书上可能写着:需要绘制一个比例为1:X的图,X可以是50也可以是100。随着项目的规模扩大,甚至会覆盖社区和城市,X此时则可能达到1000或2000。但是什么是1,什么是X?“1”是单位长度,在图中代表了现实世界中的距离x,我们以公制系统为例,1:100的比例意味着图上1cm代表现实中的100cm。计算一幅图纸的比例,则需要了解不同的单位和交叉乘法。
2-Figure Out Scale
On an architecture student’s first design assignment, it is required to draw a plan in a scale of 1:X. X can be a 50 or 100 or even a 200. As the scale of the project grows to cover neighborhoods and cities instead of buildings, the X may amount to 1000 and 2000. But what is 1 and what is x? “1” is the unit length, in a drawing, representative of a distance X in the real world. For metric system users as an example, a scale of 1:100 means that 100cm, in reality, are represented by 1cm on a drawing. Calculating a drawing’s measurements to scale requires knowledge of different units and cross multiplication.

3、适应比例
比例是任何设计成功的关键因素,这不仅仅局限于建筑设计。这就是建筑师和艺术家长期以来一直试图找出完美的比例和关系的原因,他们用以确定完美的构成或设计完美的建筑。比例是数字之间的比率,理解它们需要许多数学知识。最著名并且已经广泛应用的是黄金比例1:1.618。黄金比例之间有很强的联系,这也被称为斐波那契数列(0,1,1,2,3,5,8,13,21,34…),数学家亚瑟•本杰明在6分钟的TED演讲中进一步解释了其中有趣的关系。
3-Adjust Proportions
Proportions are vital to the success of any design and not just architectural design. That is why architects and artists have for so long been trying to figure out the perfect ratios and relations to set the perfect composition or design the perfect building. Proportions are ratios between numbers, and comprehending them requires maths knowledge. The most famous ratio which has been widely applied in architecture is the Golden ratio 1:1.618. The golden ratio has some quite strong ties to what is also known as the Fibonacci numbers (0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34 …) Mathematician Arthur Benjamin further explains this interesting relation in a quite amusing 6-minute TED Talk.

华特·迪士尼音乐厅-弗兰克·盖里/Walt Disney Concert Hall | Frank Gehry
4、编制工程量清单
工程量清单是建筑的所有部件的完整清单,例如有多少砖、多少铝窗框、多少油漆、多少瓷砖等。任何用来建造建筑和准备使用的东西都包括在工程量清单之中,当然,为了组成一个有效的清单:非常需要数学的应用。你需要知道如何计算周长、面积、体积,并将它们转化为价格。
4-Compose Bill of quantities
A bill of quantities is a complete list of all the components of a building, like for example how many bricks, how many aluminum window frames, how much paint, and how many ceramic tile. Anything and everything that was used to erect the building and make it ready for usage is included in the bill of quantities, and of course, in order to compose it you need maths. You need to know how to calculate perimeters, areas, and volumes, and translate them into prices.
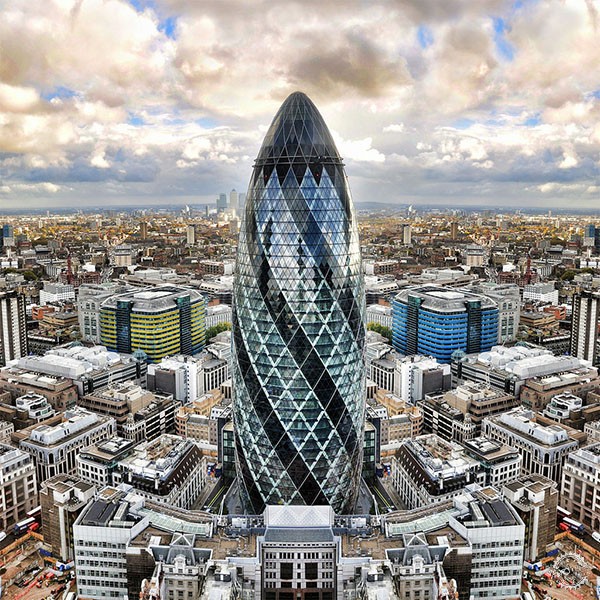

圣玛莉艾克斯30号大楼/30 St. Mary Axe, known as the Gherkin | Foster + Partners
5、创建复杂但具功能性的建筑形式
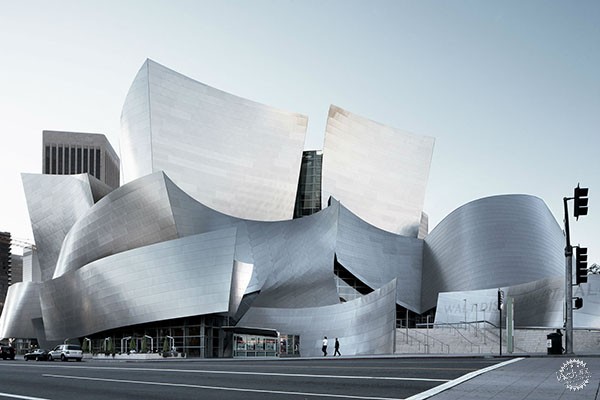
参数化设计作为现在的设计趋势之一,这是一种方法,它采用算法,随着改变变量或参数,从而产生独特的几何形式。结构的所有不同的建筑部件转化成数学定义的组件,可以使用数学方程和操作进行修改和转换。建筑师越了解几何、力学和数学原理,则越能操纵参数化设计工具,从而设计产品就越独特。著名的建筑实例中,由于在设计中的复杂数学的介入,从而产生了不平凡的建筑形体,如盖里设计的音乐厅、扎哈•哈迪德的阿利耶夫艺术中心,以及Foster 事务所设计的圣玛莉艾克斯30号大楼。
事实上,在很早的时候参数化设计已经浮出水面,著名的西班牙建筑师高迪的圣家族教堂,则运用了模拟设计方法,其特征也类似于参数化设计。
5-Create Complex yet Functional Forms
This one is achieved via what is trending now as Parametric Design. Parametric Design is a method which employs algorithms along with a set of variables, or parameters, to generate unique geometrical forms. All the different architectural parts of a structure turn into mathematically defined components which can be modified and transformed using mathematical equations and operations. The more the architect is knowledgeable of geometry, mechanics, and mathematics, the more they can manipulate the parametric design tools, and the more unique are their products. Famous architectural examples, of the involvement of complicated math in design, to render something extraordinary, are the Walt Disney Concert Hall by Frank Gehry, the Heydar Aliyev Center by Zaha Hadid, and 30 St. Mary Axe, known as the Gherkin, by Foster + Partners.
Actually, long before parametric design has surfaced as the trend of the century, the famous Spanish architect of the Sagrada Familia; Antonio Gaudi, had introduced an analog design method which features a similar mechanism to parametric design.

圣家族大教堂-安东尼·高迪/La Sagrada Familia | Antoni Gaudí
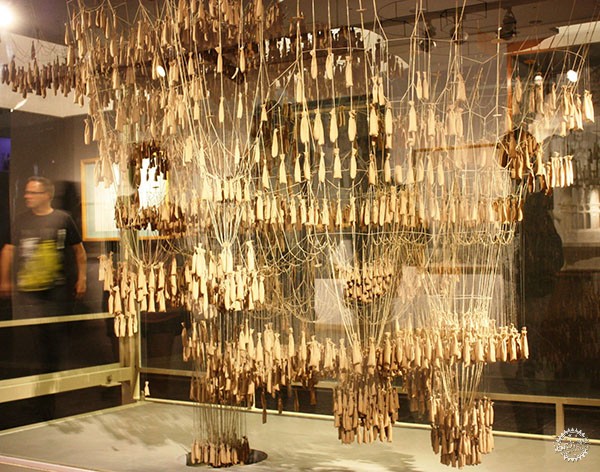

高迪圣家族大教堂的模型/The inverted model of the Sagrada Familia

阿利耶夫文化中心-扎哈·哈迪德/Heydar Aliyev Center | Zaha Hadid
出处:本文译自www.arch2o.com/,转载请注明出处。
|
|
