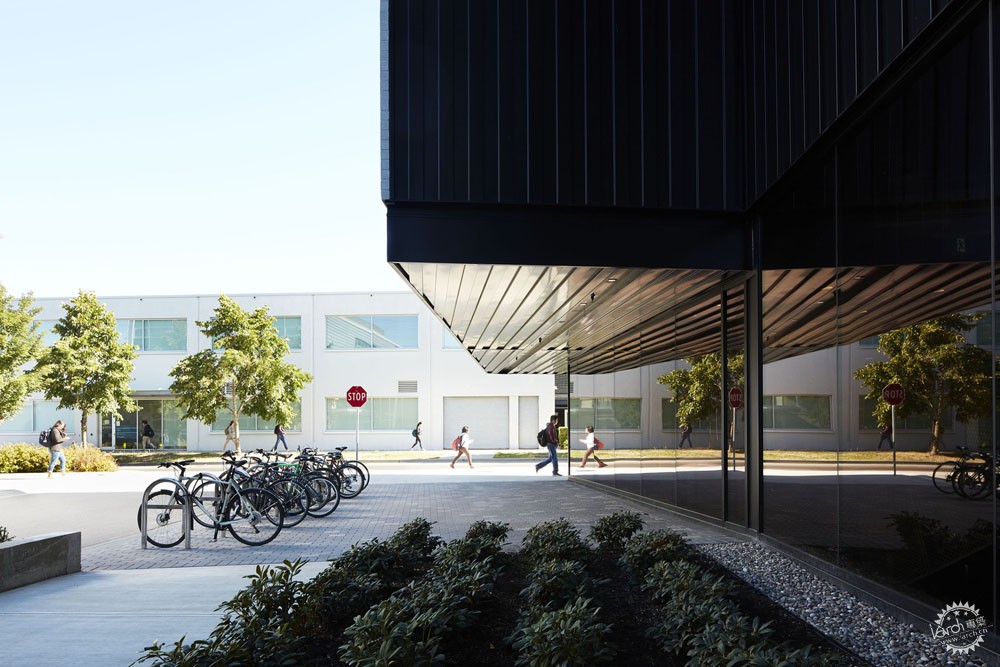

UBC Quantum Matter Institute / PUBLIC Architecture + Communication
由专筑网李韧,王帅编译
来自建筑事务所的描述:量子物质研究所服务于跨学科研究团队,主要研究微观物质。项目位于不列颠哥伦比亚大学(UBC)应用科学学院,细长的建筑体量既处于交通要道,同时也是一座连接体。而建筑师们则为这里设计了全新的入口区域,同时用作先进材料与工程实验室(AMPEL)的入口,然后将量子研究人员集中在一起,让这座研究所具有前所未有的发展潜能。就像硅是微电子产业的基础,而量子研究则能够引导诸如电子、太阳能、医学等产业的发展。
Text description provided by the architects. The Quantum Matter Institute houses an interdisciplinary group of researchers that study things at the atomic scale. Situated in the Applied Science Precinct of the University of British Columbia (UBC) campus, this slender corner addition is both a gateway and a connector. The QMI creates a new portal to the precinct, serves as a new formal entrance to the Advanced Materials and Process Engineering Laboratory (AMPEL) and collocates quantum researchers for the first time, creating the potential for research synergies in this ground-breaking field. Just as silicone was the basis of a microelectronics revolution, quantum research could lead to new industries in fields such as electronics, solar energy, and medicine.
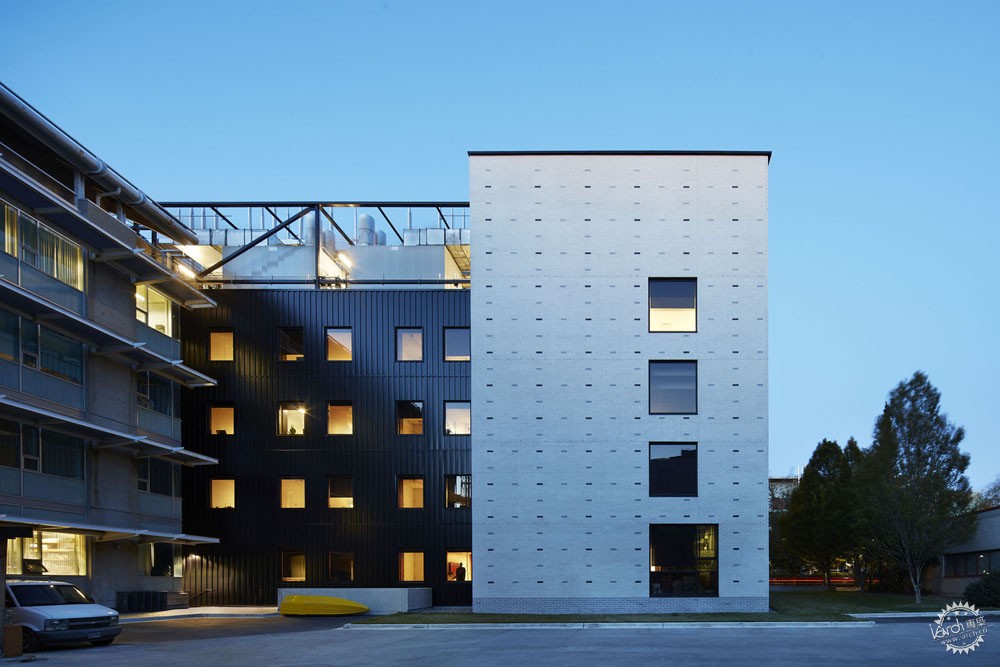

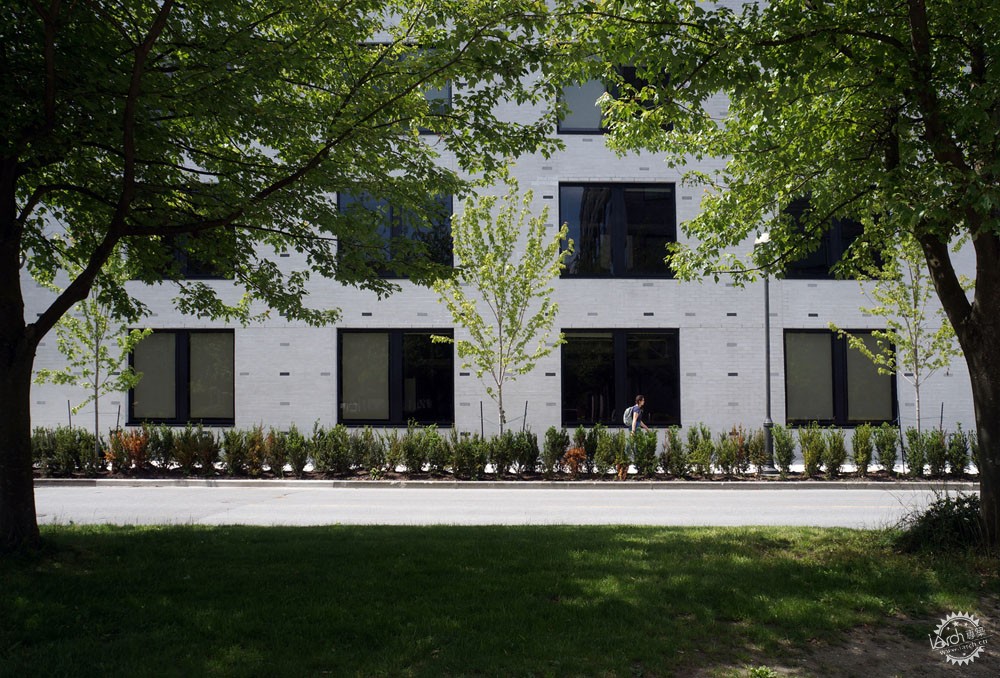
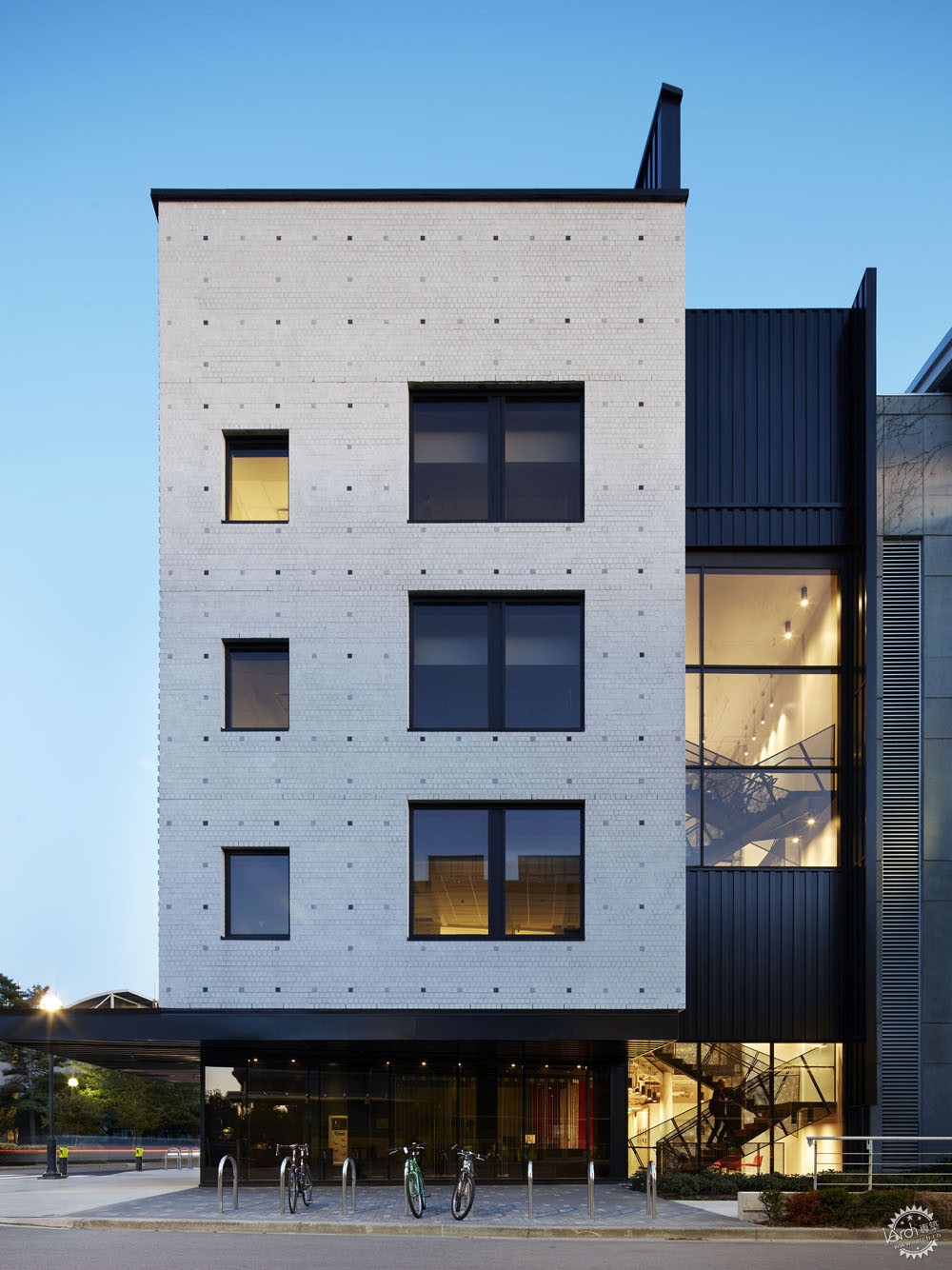
量子物质研究所在加强与周边联系的同时也增强了自身的独特性。黑灰、白色砖石与校园色彩相呼应,同时暗喻了晶体的化学成分,而这些是量子研究的主要基础。依据项目场地的限制,建筑师将建筑的角落进行切角处理,直接裸露了砖石结构,而这些砖石都由北至南统一对齐。
The QMI creates its own identity while enhancing the integrity of its neighbors. The white brick cladding mixed with black and grey relates to the campus palette while revealing the chemical compound of the crystal lattices that form the foundation for the majority of QMI’s research. The corners of the building have been chamfered as required for site constraints and reveal a crystal structure of corbelled masonry. As if affected by a giant magnet, all of the bricks align from north to south.
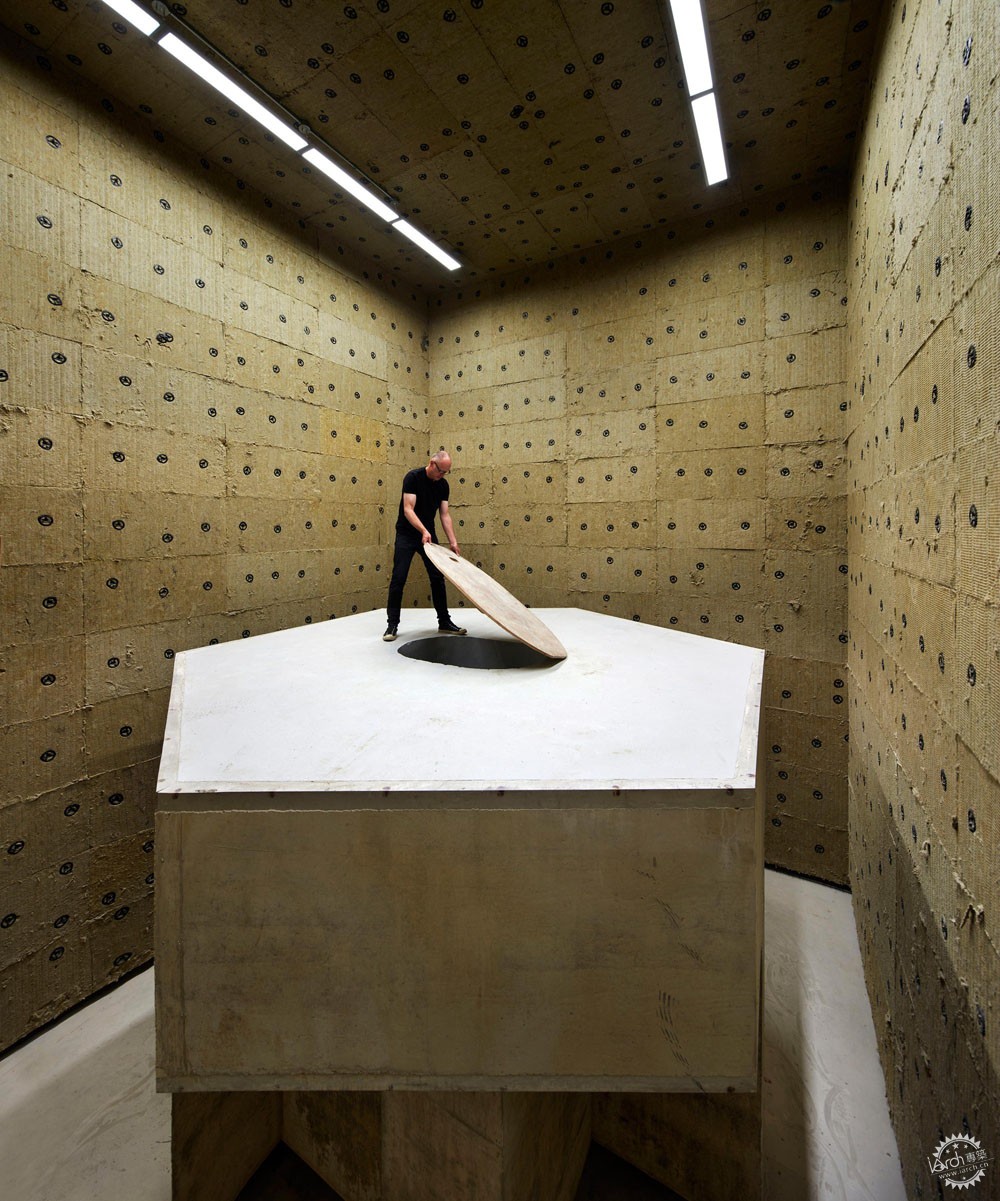

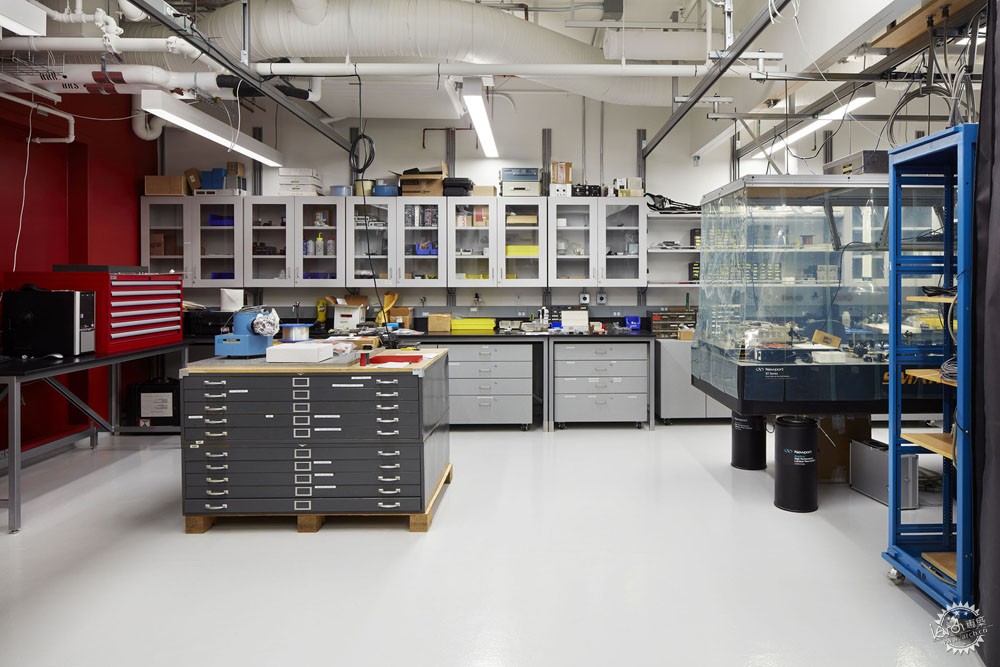
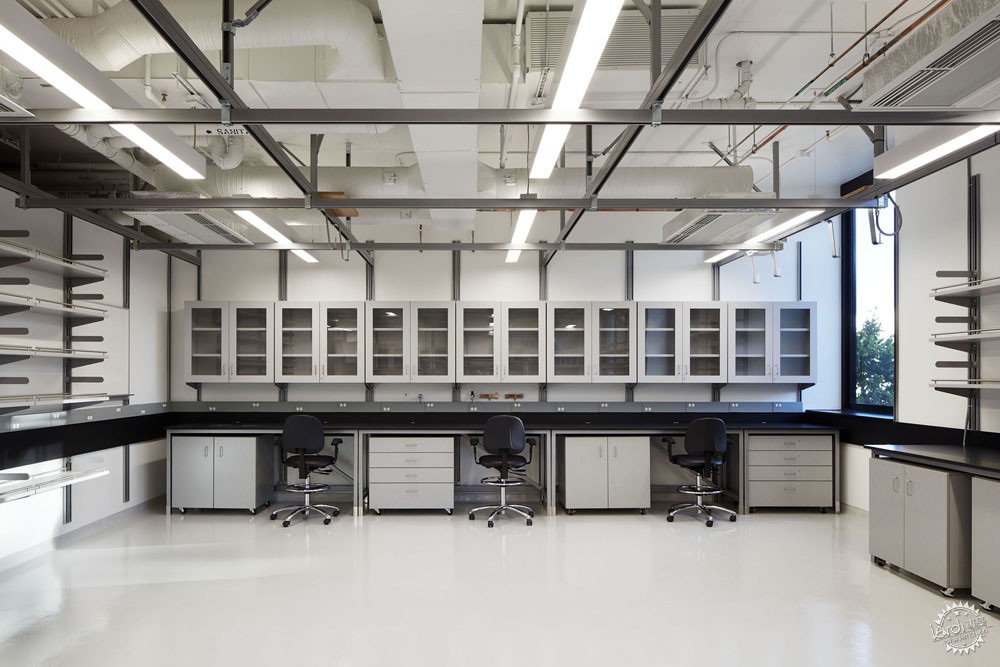
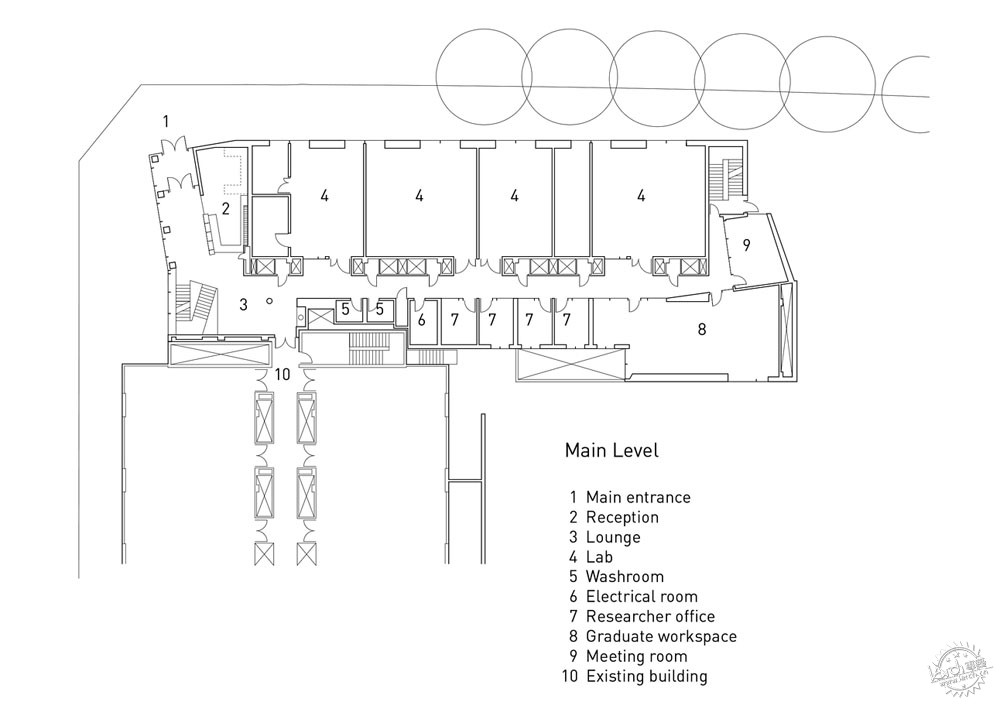
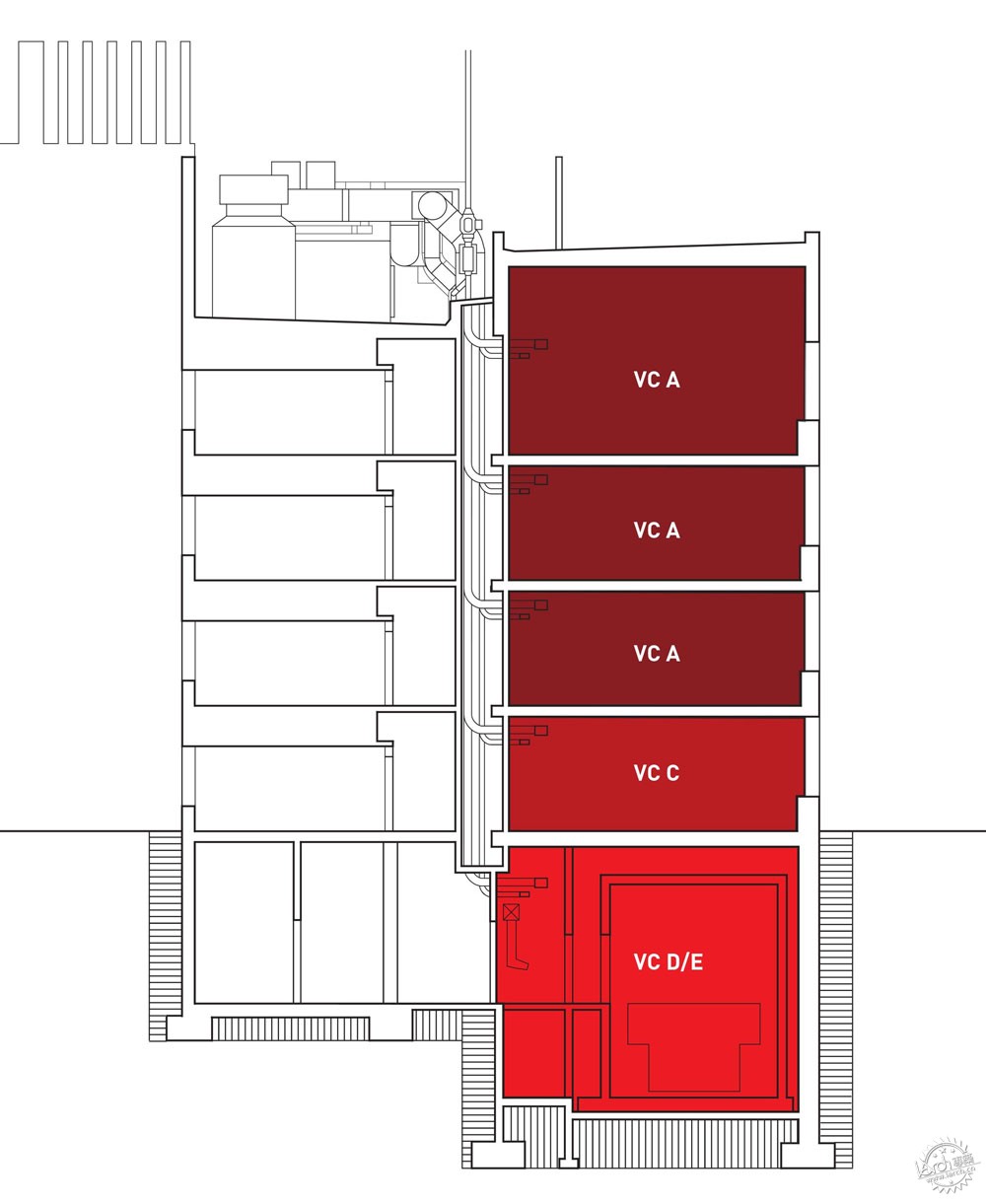
量子的研究工作一般在地下进行,因此诸如脚步等振动会对实验产生影响。而这座研究所设置有4个地下空间,以及一系列的地面实验室,这样能够依据不同的环境需求而选择实验场所。为了确保这些实验空间的抗振动性能,整座建筑通过隔离面板等材料与场地分隔开,这些实验室放置在钢筋混凝土之上,因此具有很高的灵活性,对于不同的研究活动可以有不同的布局方式。
Quantum research is best carried out underground because vibrations from sources as insignificant as a footstep can ruin an experiment. QMI has four underground vaults and a series of above-ground laboratories that provide a high degree of control over the environment. To ensure the vibration performance of these predictable spaces, the entire building is decoupled from its site with isolation pads and absorptive membranes below grade and the laboratories are stacked in a reinforced concrete structure designed to be as stiff as possible. The laboratories are designed to support long-term flexibility, acting as re-configurable stages upon which new research activities can unfold.
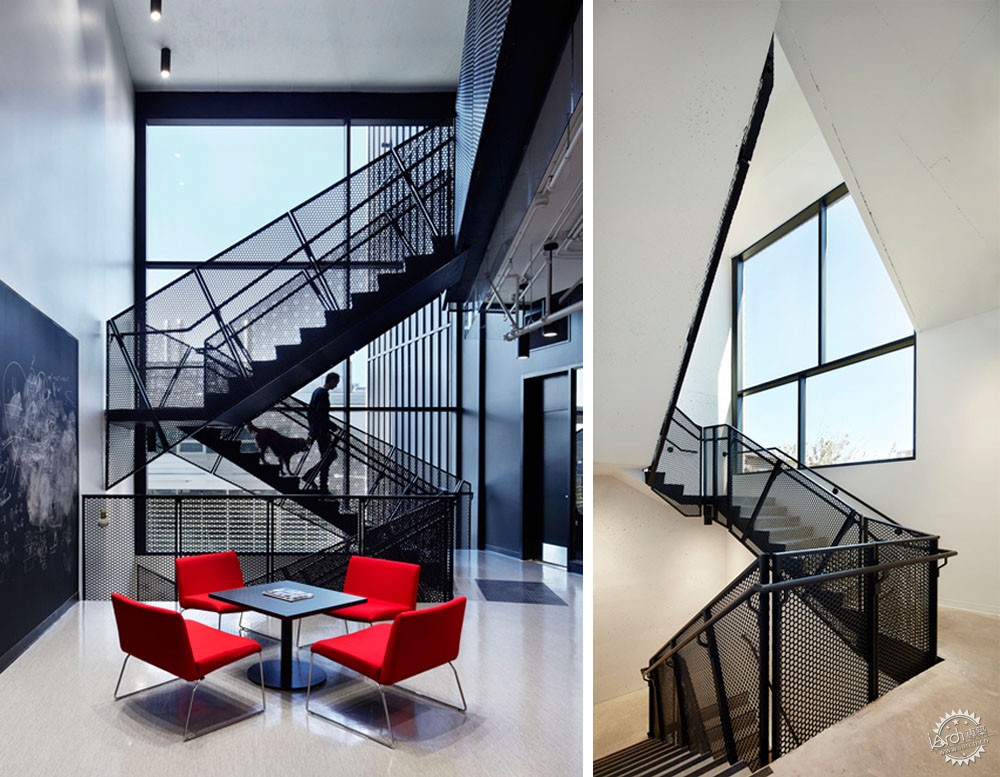


量子实验的发展非常迅速,但是量子思维的发展却并非如此,因此研究人员之间的交流对此至关重要。一位研究人员认为,思维之间的碰撞会让事情变得更加有趣,项目的灵感来源于晶体,建筑师将固定的实验空间和其他办公室、会议室、休息室放置在一起,形成流动的工作流。当研究所使用者进入或者离开一层时,他们会经过一个集散空间,这里看上去与常规空间并不相同,它是研究所与AMPEL的交界点,从而成为社会交流与思维传播的平台。
While quantum experiments flourish in vacuum chambers, the growth of quantum ideas does not. Integration between researchers is essential for new discoveries. Taking inspiration from the crystal lattices – “the interfaces are where things get interesting,” according to one researcher – the building fosters a fluid work flow by laminating predictable lab space with unpredictable offices, meeting rooms and lounges. Every time QMI users enter or leave a floor, they are momentarily taken out of their routine as they pass through a gathering space that skews and transforms the pragmatic. These gathering spaces are located at the junctures where the QMI and AMPEL meet, becoming platforms for social interaction and the cross-pollination of ideas.
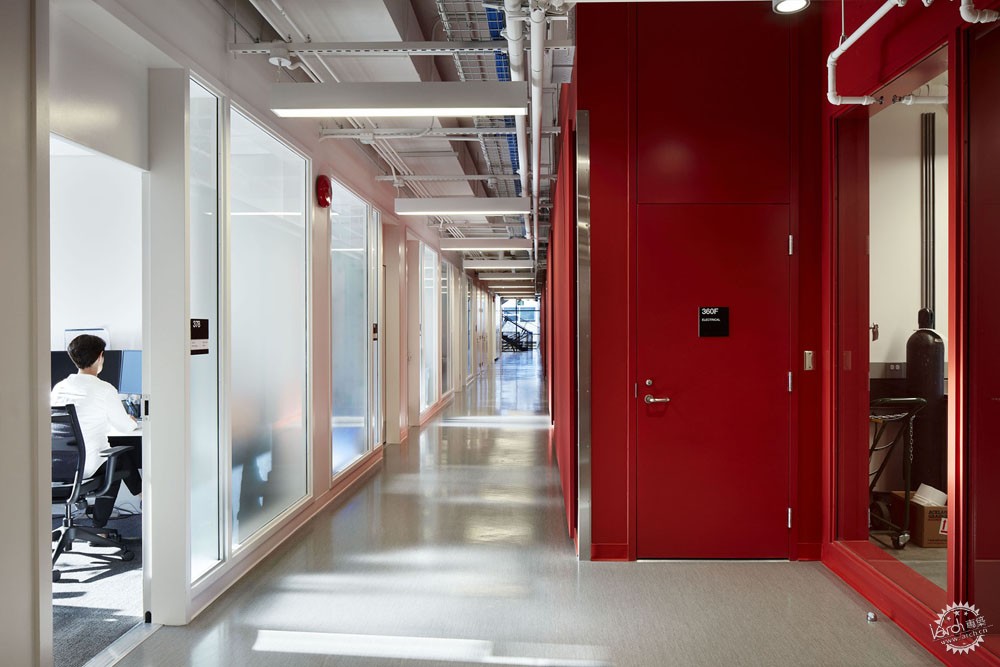
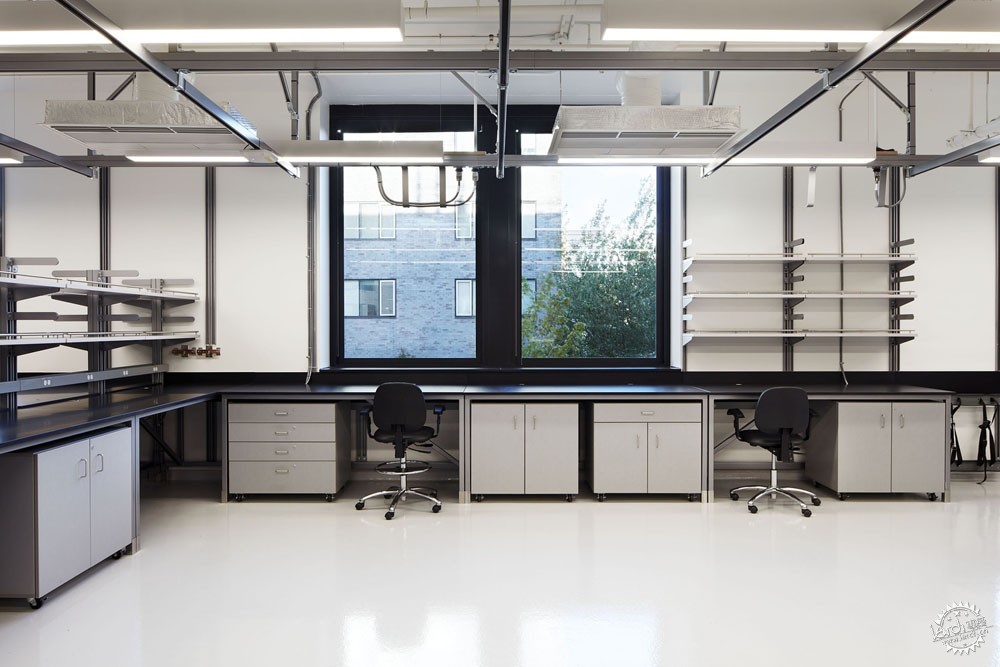



这座量子物质研究所已经过CABGC注册,并且获得金质认证。项目团队最大程度地减少了实验过程所需要的能源消耗。其中的策略包括减少实验室的气流变化,同时增强通风管理措施。
The QMI has been registered with the CAGBC and is pursuing certification at the gold level. The project team’s largest hurdle to overcome was reducing the energy consumption required by laboratory process loads. Key strategies included minimizing the number of air changes in laboratories and implementing a fume hood sash management program.


建筑设计:PUBLIC Architecture + Communication
地点:加拿大,温哥华
主创建筑师:PUBLIC: Architecture + Communication
面积:5000.0 m2
项目时间:2017年
摄影:Martin Tessler
制造商:Interface, Mecho Systems, Vicwest, Prudential
机械工程:Integral Group
结构工程:Dialog
电力工程:MMM Group Limited
岩土工程顾问:Geopacific Consultants Ltd
规范顾问:GHL Consultants Ltd.
实验顾问:Argo Architecture Inc.
声学顾问:RWDI
Architects: PUBLIC Architecture + Communication
Location: 2355 E Mall, University of British Columbia, Point Grey Campus, Vancouver, Canada
Lead Architects: PUBLIC: Architecture + Communication
Area: 5000.0 m2
Project Year: 2017
Photographs: Martin Tessler
Manufacturers: Interface, Mecho Systems, Vicwest, Prudential
Mechanical engineer: Integral Group
Structural engineer: Dialog
Electrical engineer: MMM Group Limited
Geotechnical consultant: Geopacific Consultants Ltd
Code consultant: GHL Consultants Ltd.
Laboratory consultant: Argo Architecture Inc.
Acoustic consultant: RWDI
|
|
专于设计,筑就未来
无论您身在何方;无论您作品规模大小;无论您是否已在设计等相关领域小有名气;无论您是否已成功求学、步入职业设计师队伍;只要你有想法、有创意、有能力,专筑网都愿为您提供一个展示自己的舞台
投稿邮箱:submit@iarch.cn 如何向专筑投稿?
